There is a potential for an uptick in E&A drilling activity. (Image source: Westwood)
Mozambique can still lead production and drilling in the East African Ruvuma-Rufiji (EARR) Gas Basin through to 2030, if the government continues to take strides to guarantee rapid progression of projects off Cabo Delegado province, writes Michela Francisco, analyst - onshore energy services, Westwood Global Energy Group
According to bp's 2024 Energy Outlook, global liquefied natural gas (LNG) traded volumes are forecast to grow 43% by 2030 from the 543 bn cu/m recorded in 2022
In recent years, LNG exports have been dominated by the United States, Australia and Qatar, which, according to the Energy Information Administration (EIA), held a combined LNG export capacity of approximately 257 mmtpa in 2023 (60% of total global LNG capacity). By 2030, Qatar and the US are projected to add approximately 150 mmtpa in LNG feedstock, securing the top two positions in global LNG export capacity. New additions are anticipated to stem from LNG facilities currently under construction in the US (84.1 mmtpa) and expansion phases of QatarEnergy’s North Field (65mmtpa). Despite this, there is still an appetite for additional LNG supply, given current demand expectations, making the business case for developing long-stalled gas projects from frontier areas stronger.
Mozambique and Tanzania, which house the EARR Gas Basin, could potentially be major beneficiaries of this projected demand, given abundant gas reserves (165.7 trillion cu/ft) and the basin's proximity to South-Asian import markets. However, the burning question remains – how soon can the world expect the EARR Gas Basin to roar amid an increasingly thirsty LNG demand environment?
It is pertinent to state that the EARR Gas Basin has failed to live up to its full potential due to a series of endemic bottlenecks faced in the host countries. In Tanzania, the US$40bn Tanzania LNG project, which aims to receive gas feedstock from six fields across Blocks 1 and 4 (Shell) and Block 2 (Equinor), has been subject to extensive delays due to protracted negotiations rooted in unattractive fiscal terms due to high domestic supply obligations.
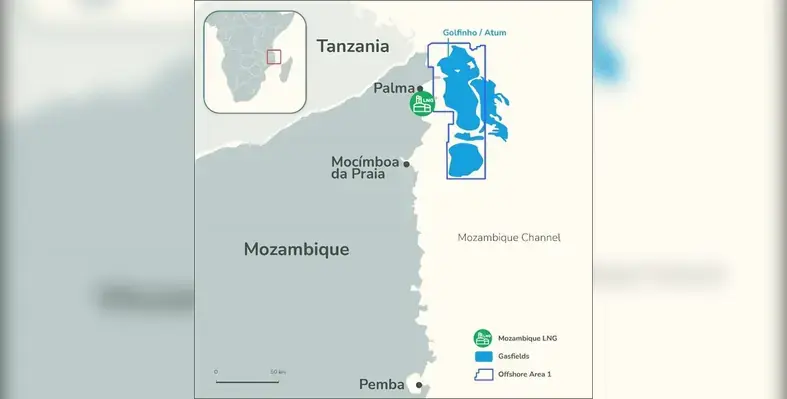
The story behind undeveloped gas reserves is quite different for the reserves offshore Mozambique, with the main culprit being the Islamist insurgency in Cabo Delgado province. The conflict has led to delays in final investment decisions (FIDs) and project start-ups, given declarations of force majeure for key projects. An example is TotalEnergies’ enforcing force majeure on the 13 mmtpa Mozambique LNG project, hereby delaying production start from the operator's Golfinho-Atum field into 2028, nine years post sanction.
On a similar note, ExxonMobil's Rovuma LNG project also felt the knock-on effect following the declaration of force majeure by TotalEnergies, given that it plans to share some facilities belonging to the Mozambique LNG project. ExxonMobil, however, seized this as an opportunity to cut costs by heavily reconfiguring the design plan from its initial two-train 15.2 mmtpa stick-build facility to an 18 mmtpa facility now being constructed using a modular approach whilst putting some emphasis on mitigating greenhouse gas emissions from the project. To date, ExxonMobil has launched tenders for a front-end engineering and design (FEED) contract and an engineering, procurement, construction and installation (EPCI) option for the subsea-to-shore gas gathering facilities.
Another factor contributing to the untimely development of resources in Mozambique is complicated project economics. TotalEnergies highlighted this in 2023 when it reported that supply chain inflationary pressures further complicated the resumption of the US$20bn Mozambique LNG project. However, there have been signs of positive developments given that TotalEnergies communicated in the company’s April 2024 earnings call that contractors have agreed to reverse contract inflation plans; thus, this is no longer an obstacle to the project’s sanctioning decision.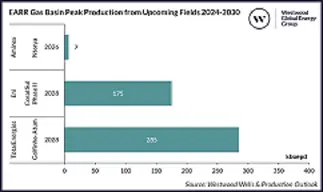
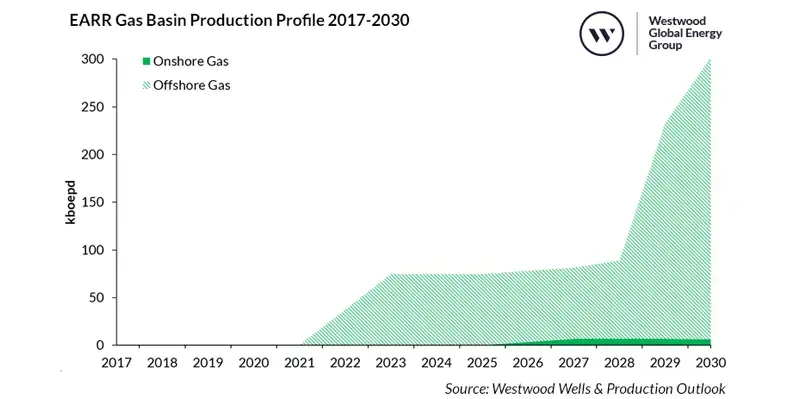
Despite these challenges, the Basin's inaugural project, Eni's 75,000 boepd Coral South floating liquified natural gas (FLNG) project, came onstream in 2022, signalling that complex, multi-billion-dollar developments could work offshore Mozambique. Output in Mozambique is forecast to remain stable at around 75,000 boepd until 2027 before growing to a peak of 295,000 boepd by 2030, up 296%, driven by TotalEnergies’ Golfinho-Atum and Eni's Coral Phase II fields.
Additionally, Tanzania's inaugural field in the Basin should come onstream in 2026 from Aminex's 7000 boepd Ntorya onshore gas field, boosting total output across the Basin to a peak of approximately 302,000 boepd by 2030, up 305% on 2023. Although there are positive signs for production, the spectre of delays that have been haunting projects remains strong, potentially diluting the positive picture prior to 2030, especially since only one of the three projects expected onstream by 2030 has passed sanctioning (TotalEnergies’ Golfinho-Atum).
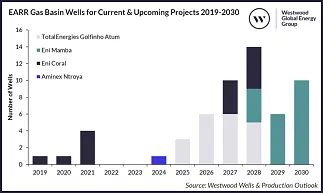
Drilling activity across both countries has been negligible, averaging one well per annum over the 2019-2024 period. Activity is anticipated to liven up over the forecast, driven by approximately 50 wells to be drilled to support upcoming LNG projects in Mozambican deepwater. Of these, 27 subsea trees have already been awarded between 2017 and 2019 for Eni’s Coral South and TotalEnergies’ Golfinho-Atum fields. 30 additional subsea trees are forecast to be awarded, with six awards anticipated for Eni’s Coral North field, scheduled to reach FID before the end of 2024. Onshore drilling activity will remain negligible, with only Aminex’s Chikumbi-1 exploration well set to be spud in 2024, the only onshore E&A well spud in the basin since 2016.
Post 2030, the outlook from the EARR Basin could be more promising, given continued interest from international energy companies (IECs), as well as licencing rounds and concession award announcements made across both countries since 2023. Although projects are few and far between in Tanzania, Shell and Equinor proposed a US$42bn LNG project from three deepwater blocks in March 2023, and this was later followed by CNOOC’s expression of interest in developing a FLNG deepwater project in blocks 4/1B and 4/1C in June 2023. From a regulatory standpoint, the current administration has increased optimism, given ongoing negotiation on fiscal terms with joint venture companies; however, nothing has materialised thus far.
Additionally, it is noteworthy to highlight the potential for an uptick in E&A drilling activity beyond Westwood’s current forecasts. This is due to the semi-autonomous Government of Zanzibar, off-Tanzania, launching its inaugural five-year licensing round in March of 2024, inviting IECs to explore eight offshore blocks.
 E&A drilling could also occur in Mozambique, given that the National Hydrocarbon Company approved a concession contract for oil exploration and production in the Angoche A6-C Area in July 2024. However, Westwood is bearish on these progressing into any E&A drilling activity before the second half of the forecast.
E&A drilling could also occur in Mozambique, given that the National Hydrocarbon Company approved a concession contract for oil exploration and production in the Angoche A6-C Area in July 2024. However, Westwood is bearish on these progressing into any E&A drilling activity before the second half of the forecast.
When dissecting current developments in the EARR Basin, it is evident that by the onset of the next decade, the Basin could contribute about 295,000 boepd of gas to meet global LNG demand. Westwood anticipates that Mozambique will continue to lead production and drilling in the EARR Basin through to 2030. However, it remains crucial for the Mozambican government to continue to take strides towards eradicating the insurgency to guarantee rapid progression of projects off Cabo Delegado province, which are currently mainly in the FEED stage.
Contrarily, on the Tanzanian side of the Basin, the portrait is more promising than in the hindcast, albeit there is still a need to focus on improving fiscal terms to attract more near-term investment and ensure that current interest from IECs is maintained. Overall, Westwood believes that by 2030, the EARR Gas Basin might start to live up to its potential as projects finally move from potential to reality.

























 E&A drilling could also occur in Mozambique, given that the National Hydrocarbon Company approved a concession contract for oil exploration and production in the Angoche A6-C Area in July 2024. However, Westwood is bearish on these progressing into any E&A drilling activity before the second half of the forecast.
E&A drilling could also occur in Mozambique, given that the National Hydrocarbon Company approved a concession contract for oil exploration and production in the Angoche A6-C Area in July 2024. However, Westwood is bearish on these progressing into any E&A drilling activity before the second half of the forecast.