In The Spotlight
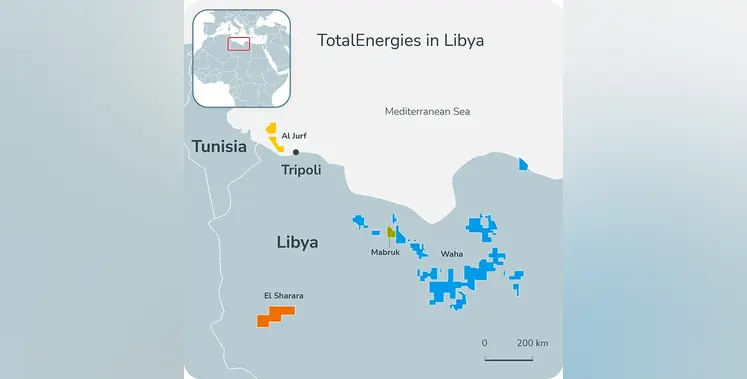
TotalEnergies has restarted production at the Mabruk oil field onshore Libya, located in concession C17, around 130 km south of Sirte
This start-up comes after 16 years, since production from the field stopped in 2015.
The construction of a new production unit with a capacity of 25,000 barrels per day was launched in May 2024. Start-up of this new facility occurred on February 28, 2026, less than two years after the project was launched.
“This restart illustrates our long-term commitment in Libya, as we celebrate TotalEnergies’ 70th anniversary in the country this year,” said Julien Pouget, Middle East and North Africa Director for TotalEnergies’ Exploration & Production business. “This project, which follows TotalEnergies’ recent announcements regarding the extension of the Waha concessions, brings low-cost, low-emissions oil production in line with the Company’s strategy, and contributes to our objective of 3% annual production growth per year until 2030.”
TotalEnergies holds an interest of 37.5% at the Mabruk.
TotalEnergies has also signed a 34-year extension agreement on the Waha Concessions onshore Libya. As the concessions continue to produce around 370,000 barrels of oil equivalent per day (boe/d), TotalEnergies plans to kickstart additional phased investments that will advance the development of the North Gialo field. This will unlock 100,000 boe/d of boosted production.
Rex-subsidiary, Lime Petroleum Holding AS, has completed hooking up the mobile offshore production unit (MOPU) and the floating storage and offloading unit (FSO) on the Seme Field in Benin
The FSO Kristina has been anchored in place as well. A flow-line has been laid from the Stella Energy 1 MOPU to the FSO. Commissioning of the production system is well underway, with oil now flowing into the FSO.
This comes as part of 100-day three-well work-programme to redevelop the Seme Field. The campaign will see the drilling of two horizontal production wells in the H6 formation (previously developed), as well as a deeper vertical appraisal well to gather data from the H7 and H8 reservoirs, to facilitate the potential advancement to Phase 2 of the development.
With all connections now in place, the company will be further conducting testing and commissioning activities to attain production optimisation and start regular production. The production start-up and optimisation in the Seme Field will be backed by additional data on the subsurface alongside the existing 3D seismic that has been reprocessed by the team.
Akrake Petroleum Benin SA holds a 76% interest in the Seme Field in Block 1, Benin, and is the operator. It is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Lime Petroleum Holding AS, an 89.74 per cent subsidiary of Rex.
The Eni-led Mozambique Rovuma Venture has signed a significant contract with Technip Energies, JGC and Samsung Heavy Industries to secure their ongoing project delivery services for the long term on the Coral Norte Floating Liquefied Natural Gas project offshore Mozambique
This follows the previously announced contract on initial activities, locking in Technip's services for the advanced stages of development as well.
The country’s second floating LNG facility, Coral Norte will be an enhanced replica of the Coral Sul project, which is currently up and running, producing over 5 million tonnes of LNG. The hull launch of Coral Norte already took place in South Korea in January.
Loic Chapuis, president - project delivery and services of Technip Energies, said, "Building on the success of Coral Sul, and together with JGC and Samsung Heavy Industries, this award further strengthens our long-standing partnership with Eni and their Area 4 partners. It also underscores our leadership in delivering innovative and complex LNG solutions to support long-term energy supply and security in Mozambique and globally.”
Replicating the same feed gas composition and field location of the Coral Sul will ensure a cost-effective and de-risked project delivery for Coral Norte, as it will be the result of proven design. This predictability at scale will ensure boosted LNG output from Coral Norte with optimal investments.
“Coral Norte is a clear recognition of Technip Energies’ engineering and project delivery expertise and our ability to replicate proven solutions with discipline and certainty," Chapuis said.
As part of phase three drilling programme offshore Gabon, Vaalco Energy has completed drilling the Etame West ET-14P exploration well
The target zone was water bearing even though 10 meters of high-quality Gamba sands were encountered in line with pre-drill predictions. Awaiting partner approval, this finding can be further pursued by utilising the well bore part to sidetrack it in the upper portion of the well. This move is expected to support the drilling of the ET-14H development well in the Main Fault Block of Etame.
The lower portion of the well will be plugged and abandoned. Operations are expected to be completed in April.
George Maxwell, Vaalco’s chief Executive Officer, said, “When we committed to drilling the Etame West exploration well, we knew there was the geologic risk of not encountering commercial sands but the size of the potential reservoir made it a risk worth taking. Furthermore, we purposely designed the well so we could still utilise the well bore to drill a development well into a known productive area if the sands were non-commercial. This side-tracked well should be completed in April.”
Vaalco has also been spudding the ET-15 infill well on the Etame platform as part of Phase Three Drilling Programme offshore Gabon.
This infill well is anticipated to significantly add to the production generation capacity of the floating storage and offloading vessel (FSO) that is operational on the Etame Block since 2022 following an extensive transition and field reconfiguration process. While a low cost solution, the FSO boasts of a high storage capacity and improved operational performance. It has helped Vaalco reach operational excellence, and production uptime and enhancement.
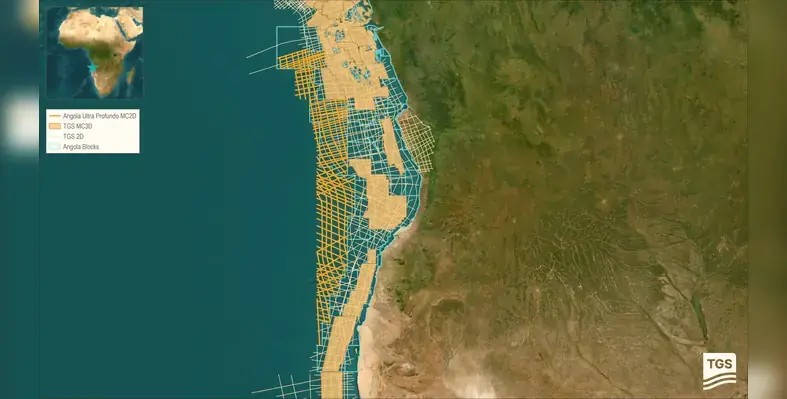
Energy data and intelligence provider, TGS, has announced the Ultra Profundo multi-client 2D survey offshore Angola
The survey spans approximately 12,600 line kilometers, and Ramform Victory began operations earlier in Q1. Data acquisition is likely to be completed in around 100 days, with fast-track products available in Q3. Full data processing is scheduled for completion in Q2 2027.
The Ultra Profundo multi-client 2D survey marks the first 2D multi-client acquisition over Angola’s ultra deep-water areas since 2015 and aims to reach previously underexplored region. The survey delivers modern, long-offset seismic data critical for imaging complex pre-salt and top-salt structures as well as basin floor channel systems, significantly enhancing regional geological understanding.
Kristian Johansen, CEO of TGS, said, “Angola’s ultra deep-water margin represents one of the most exciting frontier exploration opportunities in West Africa. Our Ultra Profundo multi-client 2D program delivers high-quality seismic coverage needed to unlock pre-salt and sub-salt potential. By leveraging TGS’ acquisition and imaging capabilities, we will provide high-quality data supporting future exploration activities.”
With all reservoir and operations risks for 2026 considered, Tullow Oil is aiming an average production rate of 34-42 kboepd, including 6 kboepd of gas
In 2025, Ntomme and Enyenra performance from TEN led the field's total production count at 16.0 kbopd, while the exit rate from Jubilee stood at 57 kbopd.
The company will be deploying riser system and riser-base gas lift for well production management activities, and waterflood and fluid lift optimisation. These, along with the support of high-uptime FPSO, five planned Jubilee wells (four producers and one water injector) are expected onstream this year. The J75-P, for instance -- where a rig has been active for drilling -- has recorded three good reservoir intervals.
The recently completed J74-P well is already onstream since January, revealing 50 meters of net pay while generating an initial gross production through the wellbore at 13 kbopd.
The well management measures align with findings from 4D seismic and Ocean Bottom Node seismic surveys to leverage significant reservoir information extracted.
Tullow has made a strategic investment to acquire the TEN FPSO as it will simplify operational synergies between the TEN and Jubilee fields, maximising output in the long term with minimal expenses. The company has already secured 10-year and 14-year-long ratifications on the West Cape Three Points and Deep Water Tano Petroleum Agreements.
Ian Perks, chief executive officer, Tullow Oil Plc, said, “2025 has been a year of disciplined execution across the business. This includes strong operational momentum which continues with excellent results from the latest Jubilee well and a further five wells due onstream this year to support our production targets. We have achieved significant cost reductions and completed the sale of non-core assets in our ongoing efforts to streamline our portfolio and strengthen our financial position.
“However our 2025 full year free cashflow was negatively impacted by the commodity price environment towards the end of the year and delays in receipt of Government of Ghana receivables and the second instalment of proceeds from the Kenya disposal.
“The refinancing transaction we have announced today enables us to focus on delivering our near-term priorities, which include driving further cost efficiencies, improving cashflow management and optimising our production."
Equatorial Guinea's national oil company, GEPetrol, has secured a heads of agreement (HoA) with American oil major, Chevron, pushing its stake in Block I's Aseng Gas Project from 5% to a whopping 32.55%
This means a big break for the country, which came following months of negotiation since the Vice President, Teodoro Nguema Obiang Mangue's visit to the United States last year.
The partnership will go a long way in well establishing the country's stronghold on its natural resources, and leveraging Aseng output, as the single field is potential of determining several downstream and upstream developments under the Extended Gas Mega Hub initiative. Alongside big projects like Alen Tail and Yoyo-Yolanda, it also unlocks access for GEPetrol in Chevron-operated blocks and potential cross-border gas flows through Gulf of Guinea pipeline infrastructure.
The agreement further ensures for GEPetrol long-term gas supply to the Punta Europa complex that will help sustain existing LNG and processing infrastructure by improving cost efficiency and reducing stranded gas. As a gas monetisation hub, this will give the Equatorial Guinea an extra edge in the global commodities market, where LNG demand continues to gain prominence.
“This agreement represents a strategic step forward for our energy sector, enhancing national participation and opening the door for further projects that will drive industrial development, create jobs and strengthen energy security for our country and the region,” said Antonio Oburu Ondo, Minister of Hydrocarbons and Mining Development of Equatorial Guinea, following the signing of the agreement at the People’s Palace in Malabo, where senior government officials, Chevron executives and the United States Ambassador were also present.
The collaboration shows Chevron's reliance on Equatorial Guinea's oil and gas industry as well as its willingness for regional integration. The major is ready to support maximum state participation, with a greater emphasis on capacity building, knowledge transfer and local workforce development, to establish mutual opportunities from the country's broader Gas Mega Hub. This also reflects Equatorial Guinea's investors-friendly policies, which are adaptive to flexible financial solutions.
Alongside Aseng-operator, Chevron, and GEPetrol, the project also includes Glencore and Gunvor.
As the Uganda National Oil Company aims to build a crude refinery, it has reached out to a unit of global commodities trader, Vitol, for a US$2bn loan to support the project alongside construction and infrastructure developments
According to Henry Musasizi, Uganda's junior finance minister, this seven-year tenor loan from Vitol Bahrain EC (VBA) comes with an interest rate of 4.92%. The minister worked on advancing the approval process for the credit line and the loan, which involved significant lawmakers, who sanctioned the development with a majority verdict.
Musasizi said that Vitol's support "presents an opportunity to access non-traditional financing to implement. ..projects and support the government in developing national infrastructure."
Vitol Bahrain EC has a long-standing presence in Uganda's downstream sector, functioning as the sole supplier of refined petroleum products to UNOC, before the state-owned company sells it to retailers across the country.
Alongside the refinery, the loan amount will also be covering road construction, a petroleum products storage terminal and extension of a petroleum pipeline from western Kenya to Uganda's capital Kampala.
Previously, the UNOC also concluded a deal with the UAE-based Alpha MBM Investments, whereby a domestic refinery with a capacity of 60,000 barrels per day is in the pipeline. The agreement accords 60% stake on the refinery to the UAE firm while UNOC retains 40%.
Uganda is looking to begin commercial oil generation starting next year from fields in its west.
Oil Review Africa catches up with Christopher Hudson, President of dmg events, ahead of ADIPEC 2025
Excerpts from an interview:
Energy across Africa, as elsewhere in the world, is seeing major shifts and advancements. How does ADIPEC 2025 reflect this changing industry landscape and help meet the needs?
Energy is one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving sectors. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global energy demand rose by 2.2% last year, outpacing the average annual increase of 1.3% recorded over the last decade. At the same time, the global population is projected to reach 9.8 billion by 2050, with over 750 million people still lacking access to electricity, and more than 2.1 billion people remain without access to clean cooking. Rising urbanisation and living standards are reshaping energy demand, with air conditioning alone expected to be one of the largest contributors to electricity demand growth in the coming decades. This reveals the sector’s increasing need to not only produce more energy but to produce it in a way that is equitable and sustainable.
In this context, ADIPEC 2025 is being held under the theme of ‘Energy. Intelligence. Impact’. It reflects a simple but powerful truth: meeting the world’s growing need for secure, affordable and sustainable energy will depend on how intelligently we harness every resource – human, technological and natural – to deliver meaningful results for economies and communities alike.
At its core, the theme recognises that intelligence – both human and artificial – is transforming the way energy is produced, managed, and consumed. From AI-driven optimisation and digital integration to advances in hydrogen, LNG, and decarbonisation, intelligent innovation is reshaping the global energy landscape. ADIPEC serves as the meeting point for these forces, where ideas translate into action and impact can be measured in investment, policy, and progress.
AI is a major topic of discussion in the context of energy, due to its high demand. How is ADIPEC responding to the challenges and opportunities of the AI-energy nexus?
Artificial intelligence is reshaping both global energy demand and the industry’s ability to respond. Data centres already consume around 1.5% of global electricity, and with AI workloads, that demand could more than double by 2030, rising from 415 TWh to 945 TWh. A single advanced AI model can require as much electricity to train as 100 households use in a year, while an AI query may consume 10 times more energy than a standard search.
This convergence is both a challenge and an opportunity. AI requires enormous energy, but it can also optimise grids, cut waste, improve operational efficiency, and accelerate decarbonisation. At ADIPEC 2025, we have expanded our AI Zone into five experiential areas showcasing how AI is transforming systems, people, and infrastructure. Alongside this, more than 80 conference sessions are dedicated to the AI–energy nexus, from predictive analytics to governance frameworks.
For Africa, this is particularly significant. Many countries are rapidly digitalising while also expanding power systems. The ability of AI to enhance reliability and reduce costs could be transformative for energy access and economic growth.
How is the diversity of the African continent and its vast energy sector reflected across ADIPEC 2025’s programme?
Africa is a core part of ADIPEC’s community. This year, we are proud to welcome a strong delegation of African ministers and leaders, including those from Nigeria, Kenya, Uganda, Sierra Leone, Zimbabwe, Gambia, Equatorial Guinea, and Egypt. Their participation enriches ADIPEC’s Strategic Conference and exhibitions, ensuring Africa’s perspectives are reflected in discussions on natural gas, hydrogen, downstream, and low-carbon solutions.
dmg events is also the largest organiser of energy and infrastructure events across Africa, with long-standing operations in Nigeria, Mozambique, Kenya, Ethiopia, Ghana, Tanzania, South Africa, Egypt and Morocco. This presence gives us a unique vantage point to bridge African priorities with global dialogue.
Africa holds some of the world’s largest reserves of natural gas, oil, and minerals, as well as enormous potential in renewables. ADIPEC is committed to supporting this potential by convening African voices alongside global leaders, unlocking partnerships that can expand access, accelerate industrialisation, and strengthen Africa’s contribution to global energy progress.
Some of ADIPEC 2025’s notable African speakers include: Honourable J. Opiyo Wandayi, Cabinet Secretary for Energy and Petroleum, Kenya; Honourable Sen. Dr. Heineken Lokpobiri, Minister for State (Oil), Petroleum Resources, Nigeria; Rt. Honourable Ekperikpe Ekpo, Minister for State (Gas) Petroleum Resources, Nigeria; Honourable Chief Adebayo Adelabu, Minister of Power, Nigeria; Honourable Julius D. Mattai, Minister of Mines and Mineral Resources, Republic of Sierra Leone; Honourable Ruth Nankabirwa Ssentamu, Minister of Energy and Mineral Development, Uganda; His Excellency Karim Badawi, Minister of Petroleum and Mineral Resources, Arab Republic of Egypt; His Excellency Antonio Oburu Ondo, Minister of Mines and Hydrocarbons, Equatorial Guinea, Honorable Julius D. Mattai, Minister of Mines and Mineral Resources, Republic of Sierra Leonne; Honourable July Moyo, Minister of Energy and Power Development, Zimbabwe; His Excellency Nani Juwara, Minister of Petroleum and Energy, Gambia; Honourable Cheikh Niane, Deputy Minister of Petroleum and Energy, Senegal, and Mathias Katamba, board chairman, Uganda National Oil Company.