In The Spotlight

Adrian Strydom, chief executive officer of the South African Oil and Gas Alliance. (Image source: South African Oil and Gas Alliance)
Africa is at a turning point in its energy journey
As cities expand and industries grow, the demand for electricity is rising fast. By 2040, Africa will need nearly 1,200 gigawatts of power, yet 600 million people still lack electricity, holding back development, healthcare, and education.
This creates a major challenge: How can Africa expand energy access without locking itself into high-emission fuels? The solution must balance affordability, sustainability, and reliability. While solar and wind power are critical, most countries lack the infrastructure to rely on them alone. Grids must remain stable, industries need steady energy, and cross-border trade requires a consistent supply. Natural gas plays a vital role in this—acting as a bridge to cleaner energy while meeting urgent electricity needs.
Africa houses about 7% of the world’s proven natural gas reserves, and production has increased by over 70% since 2000, with forecasts predicting 520 bn cu/m by 2050.
Several African countries are already benefiting from utilising natural gas reserves.
Nigeria, Africa’s largest gas producer, has over 200 trillion cu/ft of reserves, supporting millions of jobs across extraction, processing, and transportation. The Greater Tortue Ahmeyim (GTA) project in Senegal and Mauritania is attracting billions in investment, strengthening energy security. South Africa, facing a “gas cliff” due to declining imports, is exploring its local reserves to protect industrial growth. Mozambique’s Coral Sul floating LNG platform has already started production, with revenue projections reaching around US$70mn annually between 2025 and 2027. Meanwhile, the Mozambique LNG and Rovuma LNG projects hold immense potential, boasting over 100 trillion cu/ft of recoverable gas, though they remain in early development stages.
Many African countries produce only a small fraction of global emissions, yet they withstand the worst of climate change, facing extreme droughts, floods, and food insecurity. Expecting them to abandon fossil fuels without practical alternatives could slow economic development and widen inequalities. A fair energy transition must acknowledge that countries have different economic conditions and needs than major polluters. The shift to cleaner energy must be structured in a way that allows Africa to grow sustainably without compromising its ability to provide reliable power, create jobs, and strengthen its industries.
Currently, many African countries don’t have the infrastructure to rely on renewables alone. Power grids are weak, underfunded, and often unreliable. The main challenge with solar and wind energy is that they depend on the weather. If the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing, power generation drops, causing disruptions. Batteries can store excess energy for later use, but large-scale storage technology is still too expensive and not widely available.
This is where natural gas plays a crucial role. Natural gas and renewables complement each other to form a balanced and resilient energy mix. Gas provides the flexibility to fill in the gaps when renewable output is low, ensuring a constant and stable electricity supply. Additionally, gas-fired plants can ramp up quickly to meet demand and are more responsive than coal, making them ideal partners for intermittent energy sources.
It is noteworthy that the infrastructure built for natural gas today, such as pipelines and generation facilities, can even be repurposed to carry cleaner fuels like green hydrogen. This synergy allows African countries to continue scaling up renewables with confidence, knowing that natural gas is there to provide reliability, bridge energy gaps, and support the transition toward a low-carbon future.
Natural gas has been a key transitional energy source worldwide. In Africa, its role is even more critical. The continent has vast gas reserves, yet much of its potential remains untapped due to limited infrastructure investment and regulatory uncertainty. If developed strategically, natural gas can drive industrial growth, strengthen energy security, and create the capacity needed for long-term investment in renewable energy. However, unlocking this potential requires coordinated action.
Expanding gas infrastructure requires long-term investment in pipelines, processing plants, and export terminals, which take years to build. Investors need policy clarity and predictable returns, so governments must offer stable tax structures, licensing agreements, and local value retention policies to keep revenues in African economies.
Africa’s energy future must grow in a way that works for its people. Electricity must remain accessible for homes, businesses, and industries while innovative technologies develop. This is not a choice between gas and renewables - it is about using the right tools at the right time. Natural gas is a cornerstone of an orderly and just transition.
With careful planning, natural gas can support Africa’s economy today while building the foundation for a cleaner, more resilient future.
The writer of the article is Adrian Strydom, chief executive officer of the South African Oil and Gas Alliance
Akrare Petroleum Benin SA, a subsidiary of Lime Petroleum Holding, has given a detailed update of its plans with the redevelopment of the Seme Field in Block 1 offshore Benin
The Borr Gerd jack-up rig by Borr Drilling will be arriving this month as drilling is set to start early July. The following 100 days will see the drillinjg of three well-bores. The first will be an appraisal well designed to gather new data on deeper reservoir units. Afterwards, two horizontal production wells will be drilled and completed in the H6 reservoir, in which subsurface analysis has suggested significant remaining reserves, even though there has been previous production.
The company aims to complete drilling by October, when a Mobile Offshore Production Unit (MOPU) will arrive, along with a Floating Storage & Offloading unit (FSO)set to arrive mid-September. The MOPU will be hooked to the newly-drilled wells, and production is expected to start in October 2025 at production rates of approximately 16,000 barrels of oil per day (bopd).
The Seme Field redevolopment programme has been planned in phases, beginning with the production restoration stage. This runs parallel to extensive data collection activities for an optimised approach. The reprocessing of 2007 3D seismic data has been completed.
Phase 2 of the development will be evaluated to check possibilities in deeper H7 and H8 reservoirs, as well as further development drilling in the H6 reservoir.
Lime Petroleum is a subsidiary of the Singapore-based oil and gas company, Rex International Holding.
Ahead of the Kavango West 1X well excavation offshore Namibia, Reconnaissance Energy Africa Ltd has issued a public offering of its units following an agreement with Research Capital Corporation as the lead underwriter and sole bookrunner
BW Energy Limited, and directors and management members of ReconAfrica, among other investors, have generously responded to the offering. While BW Energy has already been on a strategic partnership with ReconAF, its fresh batch of investments in the company represents approximately 20% of the offering, increasing its share ownership position in ReconAfrica to around 7.6%.
The net proceeds from the offering will drive exploration activities -- mainly the Kavango West 1X well -- working capital and general corporate purposes. Work on the access road and drill site is currently being completed while the company awaits receipt of the remaining requisite permits. The rig move to the Kavango West 1X well drilling location is scheduled later this month, with drilling to begin thereafter.
Brian Reinsborough, president and CEO of ReconAfrica said, "We are excited to spud one of the Company's largest and most attractive prospects, Kavango West 1X. The results of the Naingopo exploration well announced in January 2025 increased our confidence in the potential for this well. Our teams remain very engaged with local communities and authorities to ensure a safe and efficient operation of this well."
Carl K Arnet, BW Energy CEO, said, "Our technical and operational teams at BW Energy are delighted to be participating in the high potential Kavango West 1X exploration well. BW Energy is well positioned in this strategically important energy region and further our position as a leader in Namibia's development towards energy independence. The data and insights gained through ReconAfrica's exploration campaign will further our understanding of the geology and petroleum system in Namibia and help de-risk planned exploration and development of our Kudu licence."
Nigeria International Energy Summit
Date: 25-29 February 2024
Venue: State House/ICC, Abuja
Website: https://nigeriaenergysummit.com/

The Coral South Project has contributed to 50% of Mozambique’s GDP growth in 2023. (Image source: Adobe Stock)
The progress of Mozambique's Coral South Project drove exchanges as Daniel Francisco Chapo, the President of the Republic of Mozambique, and Claudio Descalzi, Eni's chief executive officer, met in Maputo to discuss the company's ongoing and future activities in the country
The Coral South Project has contributed to 50% of Mozambique’s GDP growth in 2023 and is projected to represent 70% of GDP growth in 2024 according to the International Monetary Fund, and the recently approved Plan of Development by the Government of Mozambique, for the implementation of the Coral North FLNG project, that will enable the expansion of LNG production from the Coral reservoir in Area 4 of the Rovuma Basin.
The meeting also highlighted Eni’s strategy to diversify its activities in Mozambique, as part of its broader commitment to the country’s energy transition.
Eni has been present in Mozambique since 2006. Between 2011 and 2014, the company discovered vast natural gas resources in the Rovuma Basin, in the Coral, Mamba Complex and Agulha reservoirs, with around 2,400 billion cubic meters of gas in place.
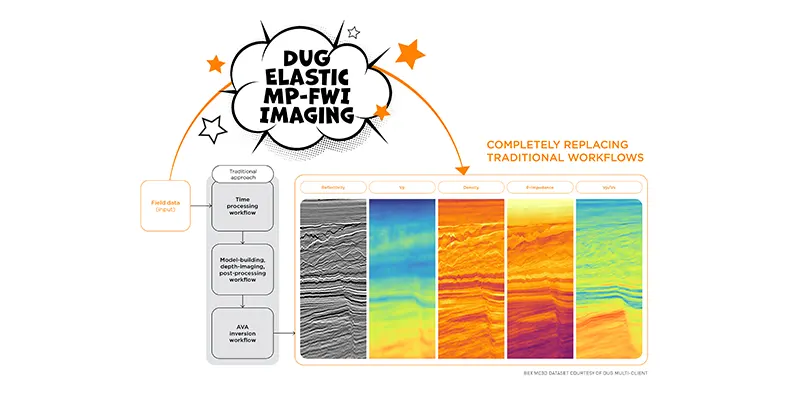
DUG Elastic MP-FWI Imaging is a unique approach to seismic processing and imaging. (Image source: DUG)
DUG has released the latest results from its elastic multi-parameter full waveform inversion (MP-FWI) imaging technology which it launched in 2022, since when more than 70 successful projects have been completed worldwide
DUG Elastic MP-FWI Imaging is a unique approach to seismic processing and imaging which is not only a complete replacement for the traditional processing and imaging workflows, it also replaces the subsequent inversion workflow for elastic rock properties.
With the traditional processing workflow, projects can take many months to years to complete. It involves the testing and application of dozens of steps such as deghosting, designature, demultiple and regularisation, all designed to overcome the limitations of conventional imaging. These workflows are complex, subjective, and very time-consuming and they rely on many assumptions and simplifications. All of these issues impact the output data quality. The resulting, primary-only data then undergoes a similarly complex model-building workflow to derive an estimate of the subsurface velocity, which is used for depth imaging. Post-migration processing is performed before the pre-stack reflectivity undergoes another workflow to derive rock properties that feed into interpretation, also relying on simplifications of the actual physics.
As well as three-component reflectivity and velocity, DUG Elastic MP-FWI Imaging enables the estimation of fundamental rock properties like P-impedance, density and Vp/Vs from field data, without the need for a secondary amplitude variation with angle (AVA) inversion step. DUG Elastic MP-FWI Imaging simultaneously resolves not only subsurface structural features but also quantitative rock property information while avoiding the need for extensive data pre-processing and (post-imaging) AVA-inversion workflows.
“Elastic MP-FWI Imaging accounts for both compressional and shear waves, handling variations in seismic wave dynamics as a function of incidence angle, including in the presence of high impedance contrasts and onshore near-surface geological complexity,” said Tom Rayment, DUG chief geophysicist. “Multiples and converted waves are now treated as valuable additional signal, increasing sampling, resolution and constraining the inverted parameters.”
DUG managing director, Dr Matthew Lamont, added, “We have invested over a decade of R&D to realise this opportunity. Our new Elastic MP-FWI Imaging technology is the product of a multi-year, significant and ongoing R&D effort, which has seen the continuous integration of complete-physics FWI imaging including viscoelasticity, anisotropy and multi-parameter updates. When using the full wavefield for simultaneous velocity model building, rock property inversion and true-amplitude imaging, a multi-parameter solution is a necessity.”
“The fact that DUG MP-FWI Imaging is delivering material imaging uplifts using field-data input is very powerful, but to couple this with high-resolution elastic rock property outputs for quantitative interpretation is even more exciting, providing immediate opportunities for new surveys and maximising the value of legacy datasets,” said Martin Stupel, geophysical manager, Geophysical Pursuit Inc.
As Tower Resources Cameroon SA prepares to drill the NJOM-3 well on the Thali license in Cameroon, it has booked the Admarine 510 jack-up rig by ADES Holding via a Letter of Award
The rig will arrive before drilling begins in Q4 2025, and is currently docked in Bahrain undergoing its five-yearly recertification project.
Built in 2019, the Admarine 510 is a GustoMSC CJ-46-X100-D triangular design three-legged jackup unit that can operate in water depth up to 375 ft.
The rig has also been contracted by Addax Petroleum for operations in Cameroon, also commencing later in the year. Tower, however, aims to use the rig before its time with Addax Petroleum.
"We are delighted to make this award, and are looking forward to working with ADES on the NJOM-3 well this year. Our rig selection process has been made a little more complex by the opportunity to coordinate our timing with that of other nearby oil and gas companies, including Addax Petroleum in particular, however I believe it has resulted in a very good commercial outcome for all parties," said Jeremy Asher, CEO and chairman of Tower Resources.

Adrian Strydom, chief executive officer of the South African Oil and Gas Alliance. (Image source: South African Oil and Gas Alliance)
Africa is at a turning point in its energy journey
As cities expand and industries grow, the demand for electricity is rising fast. By 2040, Africa will need nearly 1,200 gigawatts of power, yet 600 million people still lack electricity, holding back development, healthcare, and education.
This creates a major challenge: How can Africa expand energy access without locking itself into high-emission fuels? The solution must balance affordability, sustainability, and reliability. While solar and wind power are critical, most countries lack the infrastructure to rely on them alone. Grids must remain stable, industries need steady energy, and cross-border trade requires a consistent supply. Natural gas plays a vital role in this—acting as a bridge to cleaner energy while meeting urgent electricity needs.
Africa houses about 7% of the world’s proven natural gas reserves, and production has increased by over 70% since 2000, with forecasts predicting 520 bn cu/m by 2050.
Several African countries are already benefiting from utilising natural gas reserves.
Nigeria, Africa’s largest gas producer, has over 200 trillion cu/ft of reserves, supporting millions of jobs across extraction, processing, and transportation. The Greater Tortue Ahmeyim (GTA) project in Senegal and Mauritania is attracting billions in investment, strengthening energy security. South Africa, facing a “gas cliff” due to declining imports, is exploring its local reserves to protect industrial growth. Mozambique’s Coral Sul floating LNG platform has already started production, with revenue projections reaching around US$70mn annually between 2025 and 2027. Meanwhile, the Mozambique LNG and Rovuma LNG projects hold immense potential, boasting over 100 trillion cu/ft of recoverable gas, though they remain in early development stages.
Many African countries produce only a small fraction of global emissions, yet they withstand the worst of climate change, facing extreme droughts, floods, and food insecurity. Expecting them to abandon fossil fuels without practical alternatives could slow economic development and widen inequalities. A fair energy transition must acknowledge that countries have different economic conditions and needs than major polluters. The shift to cleaner energy must be structured in a way that allows Africa to grow sustainably without compromising its ability to provide reliable power, create jobs, and strengthen its industries.
Currently, many African countries don’t have the infrastructure to rely on renewables alone. Power grids are weak, underfunded, and often unreliable. The main challenge with solar and wind energy is that they depend on the weather. If the sun isn’t shining or the wind isn’t blowing, power generation drops, causing disruptions. Batteries can store excess energy for later use, but large-scale storage technology is still too expensive and not widely available.
This is where natural gas plays a crucial role. Natural gas and renewables complement each other to form a balanced and resilient energy mix. Gas provides the flexibility to fill in the gaps when renewable output is low, ensuring a constant and stable electricity supply. Additionally, gas-fired plants can ramp up quickly to meet demand and are more responsive than coal, making them ideal partners for intermittent energy sources.
It is noteworthy that the infrastructure built for natural gas today, such as pipelines and generation facilities, can even be repurposed to carry cleaner fuels like green hydrogen. This synergy allows African countries to continue scaling up renewables with confidence, knowing that natural gas is there to provide reliability, bridge energy gaps, and support the transition toward a low-carbon future.
Natural gas has been a key transitional energy source worldwide. In Africa, its role is even more critical. The continent has vast gas reserves, yet much of its potential remains untapped due to limited infrastructure investment and regulatory uncertainty. If developed strategically, natural gas can drive industrial growth, strengthen energy security, and create the capacity needed for long-term investment in renewable energy. However, unlocking this potential requires coordinated action.
Expanding gas infrastructure requires long-term investment in pipelines, processing plants, and export terminals, which take years to build. Investors need policy clarity and predictable returns, so governments must offer stable tax structures, licensing agreements, and local value retention policies to keep revenues in African economies.
Africa’s energy future must grow in a way that works for its people. Electricity must remain accessible for homes, businesses, and industries while innovative technologies develop. This is not a choice between gas and renewables - it is about using the right tools at the right time. Natural gas is a cornerstone of an orderly and just transition.
With careful planning, natural gas can support Africa’s economy today while building the foundation for a cleaner, more resilient future.
The writer of the article is Adrian Strydom, chief executive officer of the South African Oil and Gas Alliance
A thriving local refining sector requires a skilled workforce, which translates into job creation across various levels, from engineers and technicians to construction workers and administrative staff
The development of local refineries can also stimulate growth in related industries, such as transportation, logistics and service sectors, further amplifying employment opportunities.
Building a robust petrochemicals industry enables countries to diversify their economies. Petrochemicals serve as essential inputs for numerous sectors, including agriculture (fertilisers), manufacturing (plastics), and pharmaceuticals. By investing in this industry, countries can reduce their reliance on a single commodity – oil – and create a more resilient economic structure.
By minimising crude oil exports and focusing on value addition, nations can create jobs and stimulate economic growth. This comprehensive strategy not only enhances national wealth but also contributes to the overall well-being of African populations, aligning economic success with social progress.
The concept of ‘profit versus purpose’ serves as a guiding principle in the ongoing debate about energy policy. This framework integrates economic objectives with social and environmental goals, demonstrating that financial success and societal benefit are not mutually exclusive. By prioritising investments that address energy poverty and promote social equity, businesses can contribute to the continent's sustainable development while remaining economically viable.
Investing in energy solutions in underserved regions presents unique challenges, including high initial costs and limited access to traditional financing. However, these challenges also create opportunities for innovative financing mechanisms. Multilateral finance institutions and climate finance initiatives can play the central role in mobilising resources and sharing financial burdens.
Shared value mechanisms allow companies to align their business operations with social impact goals, unlocking new market opportunities while addressing critical issues like energy access. Investing in off-grid renewable energy solutions, for instance, can enable companies to tackle energy poverty while expanding their market reach.
The pathway to unlocking Africa’s oil and gas potential lies in balancing effective governance with the principles of profit for purpose. African governments must create policies that not only attract sustainable investment but also prioritise the welfare of their citizens.
By implementing transparent frameworks, favourable fiscal terms, and innovative financing models, African countries can harness their natural resources for the greater good. This collective responsibility to promote sustainable development will ensure that the benefits of oil and gas investments extend beyond profit, enriching communities and driving long-term economic growth across the continent.
This is the last of a two-part article written by Taona Kokera, director - head of infrastructure finance advisory at Forvis Mazars in South Africa
As Africa is zooming in on brownfield sites for maximum oil recovery, artificial intelligence and machine learning technologies are fuelling the industry's optimisation goals
Redifining operational efficiency by extending field life and maximising output, AI is set to move the oil and gas industry at a US$6.4bn market value by 2030.
As major operators increasingly adopt AI, global oilfield technology companies like Baker Hughes, Halliburton or SLB have opened bases in Africa. SLB's technology is backing several billion-dollar oil projects in Angola, and has introduced the Africa Performance Centre in Luanda this year. It has a strong presence in other regions of Africa as well.
Repsol has several developments underway in Libya, Algeria and Morocco and strives to bolster production across these markets.
Enhanced oil recovery is currently witnessing a disruption as AI has unlocked access to large datasets which is unimaginable with traditional systems. This makes a huge difference for operators in taking the right decisions. With deep geological and production data in hand, reservoir management and pattern identification become much simpler.
AI is now way past the experimental stage, and is being adopted on a policy level as well. Many African countries are streamlining policy to support EOR at legacy assets. Angola, for example, implemented its Incremental Production Initiative in 2024 which offers tax incentives to encourage reinvestments in mature oilfields. Energy major ExxonMobil made the first discovery – the Likembe-01 well - as part of the initiative in 2024, demonstrating the role policy plays in unlocking incremental resources. The African Union Commission also declared AI as a strategic priority for the continent in May 2025, citing the role machine-learning plays in transforming the continent’s development trajectory.
These topics will drive conversations at the African Energy Week (AEW): Invest in African Energies 2025 that will be taking place from 29 September 29 to 3 October in Cape Town.